The world economy is feeling the heat as U.S. President Donald Trump’s trade tariffs continue to escalate. The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) has warned that these trade barriers are not only slowing down economic growth but also fueling inflation.
The Global Economic Impact of U.S. Trade Tariffs
The OECD’s latest economic forecast reveals that several major economies, including the U.S., Canada, and Mexico, will suffer from the ongoing trade disputes. While Trump imposed hefty tariffs on steel and aluminum imports—25% across the board—the ripple effects are being felt worldwide.
Some of the hardest-hit nations are Canada and Mexico, primarily due to their close trade ties with the United States. These countries have been at the receiving end of some of the highest tariffs, which are now threatening their economic stability.
OECD’s Downgrade of Growth Predictions
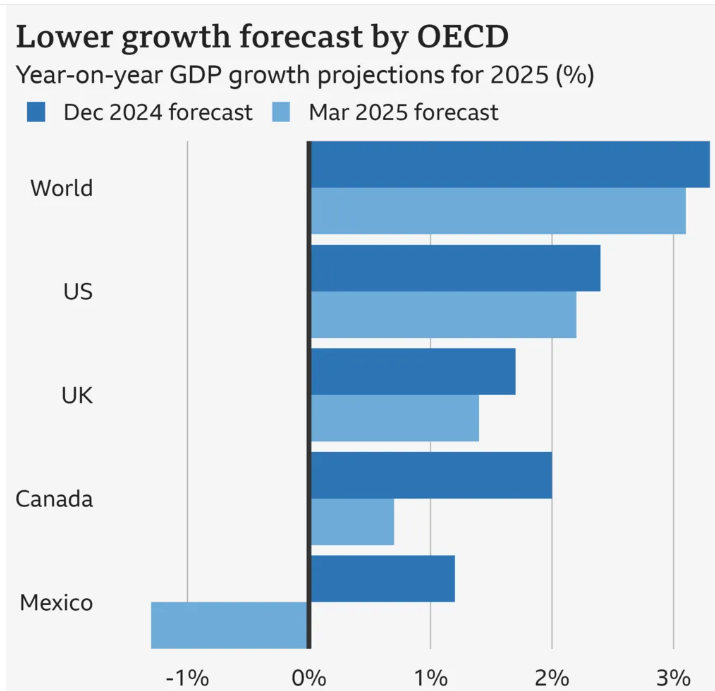
The OECD has made significant cuts to its economic growth projections for multiple countries. According to its latest forecast:
Canada’s growth is expected to slow to just 0.7% this year and in 2026, down from the previously predicted 2% for both years.
Mexico faces a potential recession, with the economy expected to shrink by 1.3% this year and another 0.6% next year. This is a drastic change from earlier projections, which had Mexico growing at 1.2% and 1.6%.
The U.S. economy will also take a hit, with growth now expected to be 2.2% this year and 1.6% in 2025—lower than the earlier forecast of 2.4% and 2.1%.
China, on the other hand, has seen a slight upward revision, with growth now projected at 4.8%, despite U.S. tariffs targeting Chinese goods.
Inflation on the Rise Due to Tariffs
One of the biggest concerns surrounding these tariffs is their impact on inflation. As higher import taxes drive up the cost of goods, consumers and businesses are left facing increased prices. The OECD has warned that global inflation could remain higher for longer than previously anticipated.
For instance, across 20 of the world’s largest economies, inflation is now expected to hit 3.8% this year—up from the previously projected 3.5%. This means that consumers will likely continue to feel the pinch when purchasing everyday goods and services.
Canada and the EU Fight Back with Retaliatory Tariffs
In response to Trump’s aggressive tariff policies, both Canada and the European Union have announced their own retaliatory measures. By imposing tariffs on U.S. goods, these countries are attempting to counterbalance the economic strain placed upon them.
However, the OECD has cautioned that this tit-for-tat trade war could lead to even more uncertainty in the global market. Higher trade barriers and unpredictable policies make it harder for businesses to plan their investments, ultimately slowing economic growth worldwide.
The Growing Threat of a Fragmented Global Economy
The OECD has emphasized that the world economy is becoming increasingly fragmented due to these trade conflicts. This fragmentation is a serious concern as it disrupts global supply chains, making it more expensive and difficult for businesses to operate efficiently.
A key risk identified by the OECD is the possibility of even higher and broader tariffs being imposed, which would further stifle growth and drive up inflation.
The World Economy is Slowing Down
According to the OECD, global economic growth is set to decelerate from 3.2% in 2024 to 3.1% in 2025. This slowdown is largely attributed to trade tensions and rising interest rates. As central banks attempt to control inflation, borrowing costs remain high, making it harder for businesses and consumers to spend freely.
While inflation is expected to ease gradually, the OECD has warned that it may not slow down as much as previously hoped. Higher costs of goods and services could persist longer than anticipated, putting additional strain on both businesses and households.
Elon Musk’s Tesla Sounds the Alarm on U.S. Tariffs
Even major corporations are raising concerns about the impact of Trump’s tariffs. Tesla, the electric vehicle giant owned by Elon Musk, has publicly stated that U.S. exporters—including Tesla itself—are at risk of serious financial harm if foreign countries retaliate against these tariffs.
In a letter to the U.S. Trade Representative, Tesla highlighted the dangers of trade barriers, emphasizing that they could reduce competitiveness for American businesses on the global stage.
The UK’s Economy Also Feels the Impact
Beyond North America, the UK is also experiencing a slowdown in economic growth due to global trade disruptions. The OECD has cut its growth forecast for the UK:
2025 growth forecast lowered to 1.4%, down from the earlier projection of 1.7%.
2026 growth forecast reduced to 1.2%, slightly down from 1.3%.
While these figures are still higher than the Bank of England’s more pessimistic outlook (which has predicted just 0.75% growth in 2025), they highlight the widespread economic strain caused by the trade disputes.
Looking Ahead: What’s Next for Global Trade?
As tensions between major economies continue, experts warn that the world could see prolonged economic instability. Here are some potential future scenarios:
Further Retaliation from Affected Countries
If Canada, Mexico, China, and the EU impose additional tariffs on U.S. goods, global trade could slow even further.
Higher Inflation and Interest Rates
With the cost of imports rising, central banks may keep interest rates high for longer to combat inflation, making borrowing more expensive for businesses and consumers.
Trade Negotiations or Policy Shifts
There is a possibility that governments could negotiate new trade agreements to ease tensions. However, given the current political landscape, this remains uncertain.
Shifts in Global Supply Chains
Businesses may begin diversifying their supply chains, reducing reliance on countries affected by tariffs. This could lead to increased production costs and delays in global trade.
Final Thoughts
The escalating trade war initiated by President Trump has already left a noticeable mark on the global economy. With growth slowing, inflation rising, and businesses struggling to navigate uncertain policies, the outlook remains challenging.
While some countries, like China, have managed to show resilience, others—particularly Canada and Mexico—are facing severe economic consequences. The ongoing trade tensions have created a fragmented global market, which could have long-lasting effects on international business and financial stability.
As we move forward, policymakers and business leaders will need to carefully assess the risks and take proactive measures to stabilize the economy. Whether this means renegotiating trade deals, diversifying supply chains, or finding alternative strategies to mitigate economic damage, one thing is clear: the world is watching closely as trade policies continue to shape the future of global commerce.
